If you’re like me and didn’t gain much insight during sex-ed class about your period – you’re not alone.
I’m here to finally give you the spiel on what you’ve been waiting for.
Before we dive into our Period Blog Series, I think it’s important to go over some terminology that will appear in upcoming posts. This way, this blog can always be a place of reference if you’re in need of a refresher!

“Your period is not just your period. It is an expression of your underlying health. When you are healthy, your menstrual cycle will arrive smoothly, regularly, and without symptoms. When you are unhealthy in some way, your cycle will tell the story” – Lara Biden ND
Basically, based on how often we get it, how we get it, how heavy it is, the amount of pain/discomfort we experience, our bodies are giving us signs of what’s truly going on. We’ll discuss this in future blogs to come.
I’m here to tell you that the symptoms you experience are very common but not normal.
As much as the time of the month is a real pain in the uterus (pun intended) – your period is providing you insight into your health. Let’s start paying attention.
Here’s a short list of the terminology that will be used.
Menstrual Glossary
Fallopian Tube: One of the two tubes on either side of the uterus that carry the egg from an ovary to the uterus
Follicle-Stimulation Hormone (FSH): A hormone that stimulates the maturation of the ovarian follicles in preparation for ovulation
Follicular phase: The first half of the menstrual cycle (starts the day of menstruation and ends with ovulation begins). In this phase, estrogen is high, and the ovarian follicles mature in preparation for ovulation.
Luteal Phase: The second half of the menstrual cycle that occurs after ovulation and progesterone is higher.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH): A hormone that triggers ovulation and the development of corpus luteum (tissue that forms in the ovary after ovulation)
Estrogen: A female sex hormone produced by the ovaries and is dominant in the first half of the menstrual cycle
Ovaries: The female reproductive organ that produces eggs and hormones
Ovulation: When the ovary releases an egg.
Ovulatory Phase: The time between the follicular and luteal phases when LH surges (triggering the release of an egg)
Progesterone: A hormone that helps regulate your cycle. It helps thicken the lining of the uterus to prepare for a potential fertilized egg.
Testosterone: A sex hormone secreted by the ovaries and adrenal glands that rises before ovulation. It is highest in men but is also necessary for women
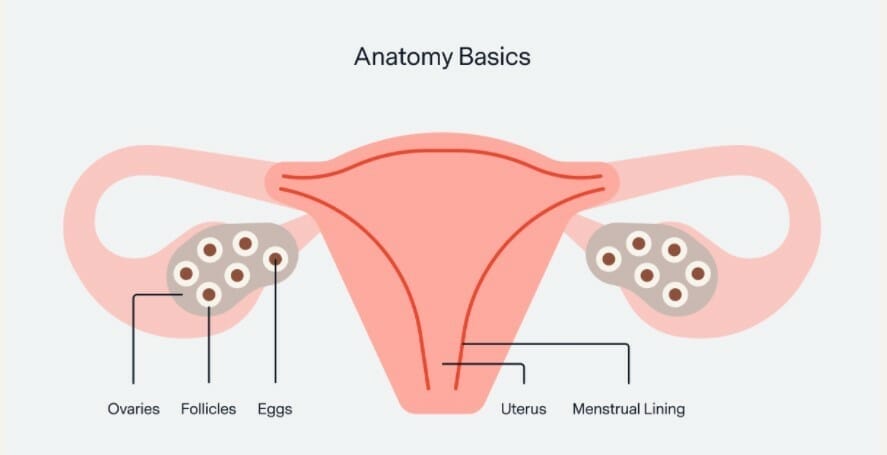
Now that we got some of the important lingo out of the way, our next blog will be breaking down the monthly cycle. Remember your period isn’t just the days you bleed, it’s also what happens the rest of the month!

